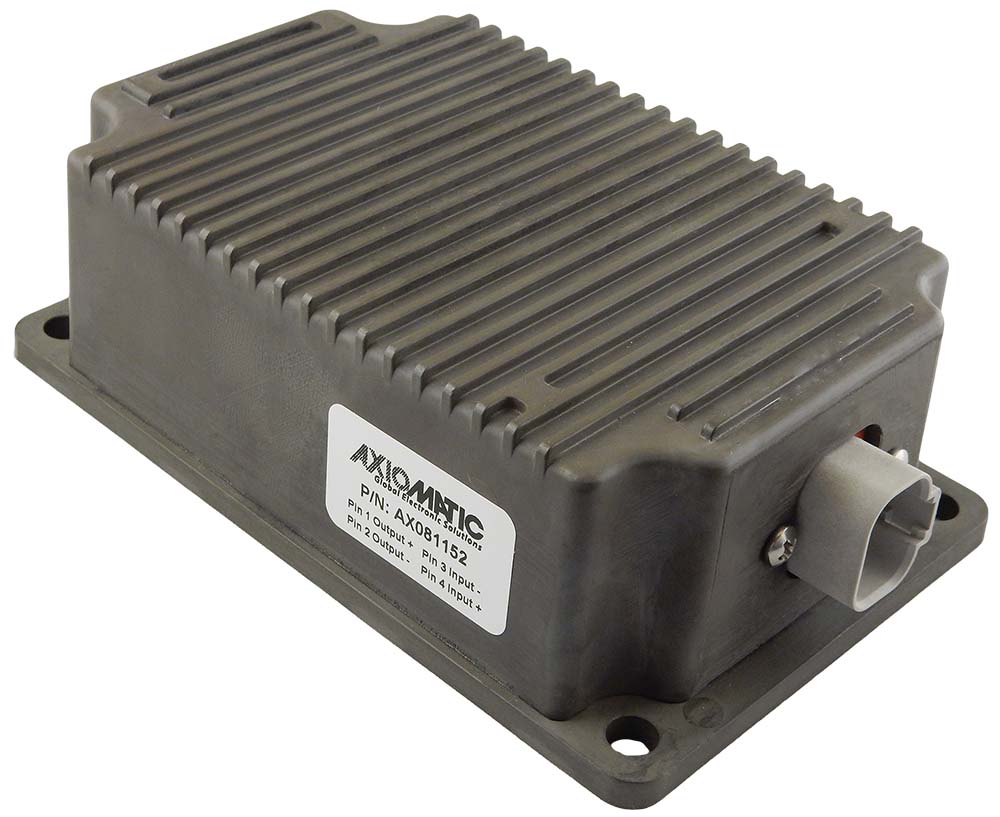
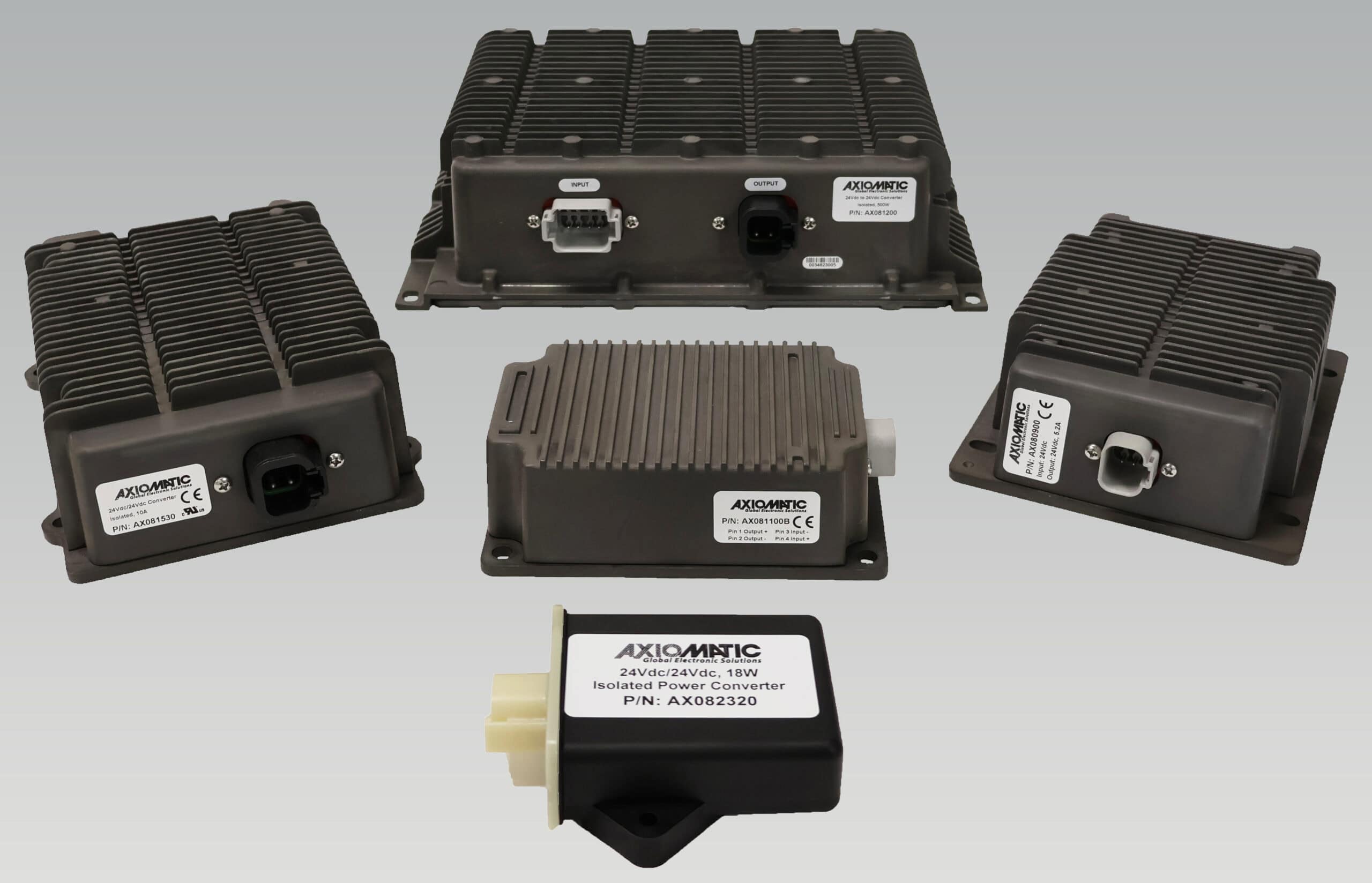
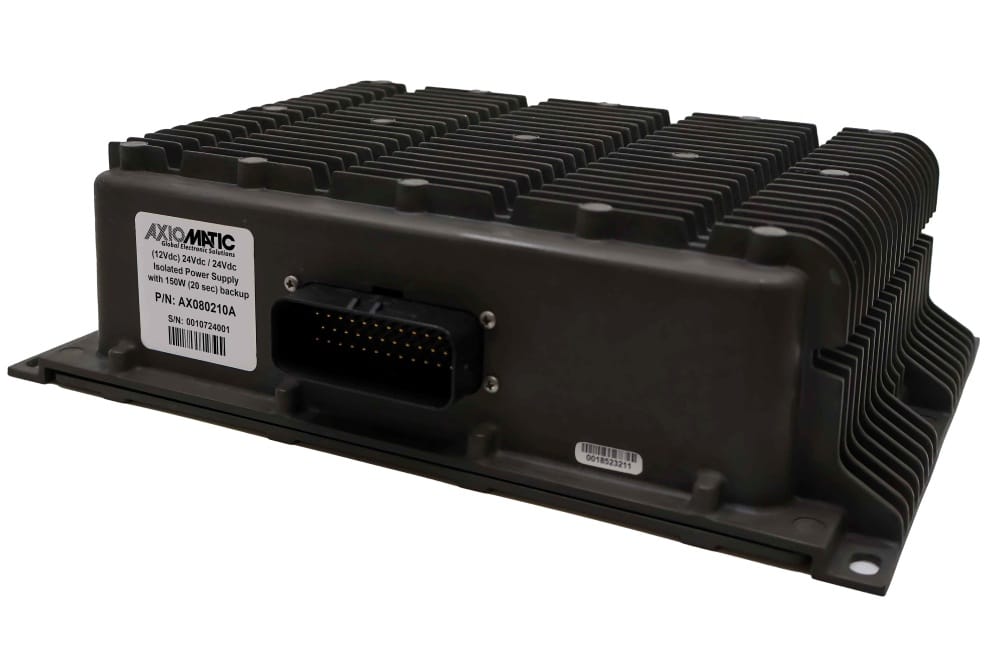
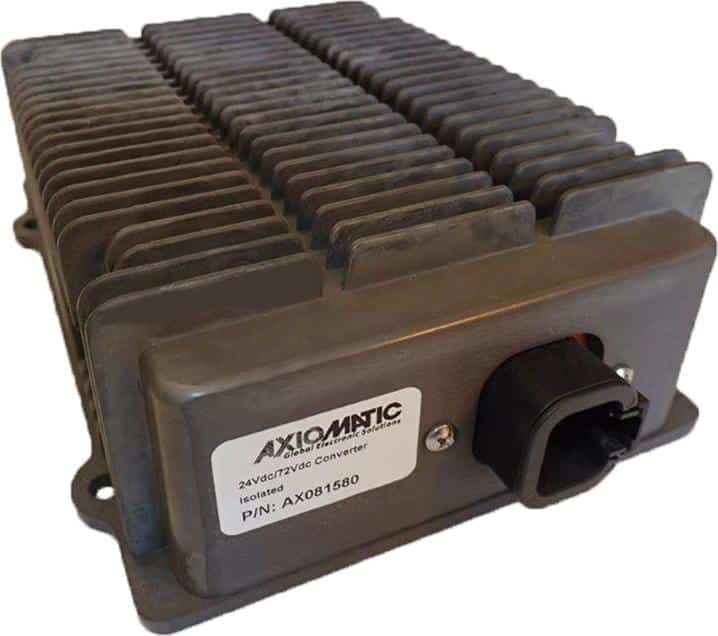
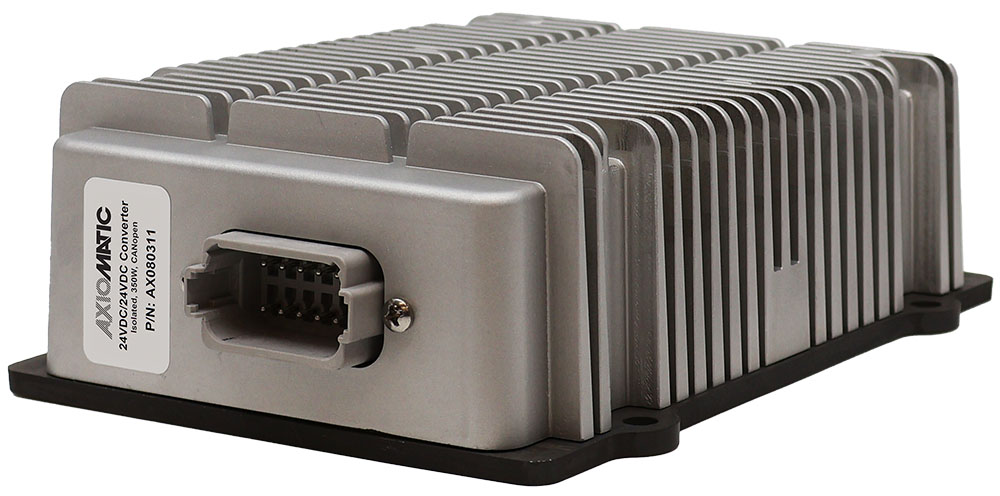
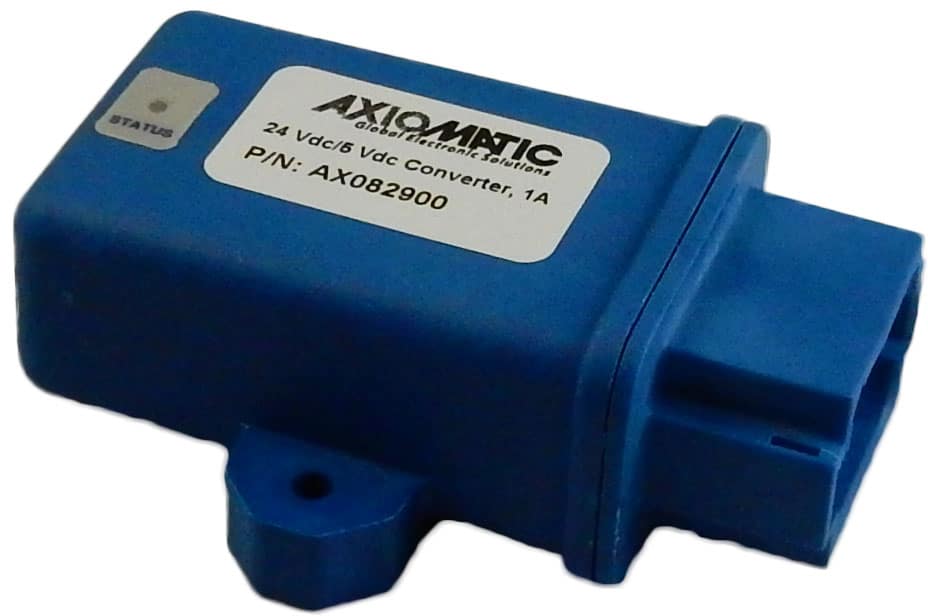
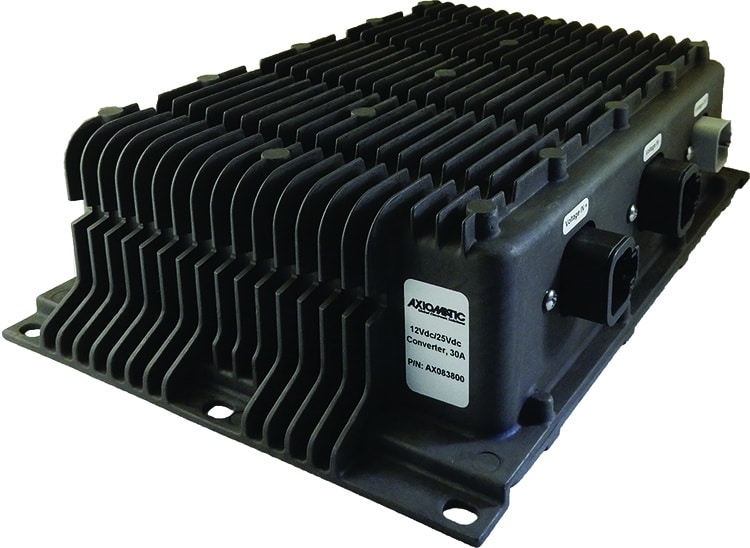
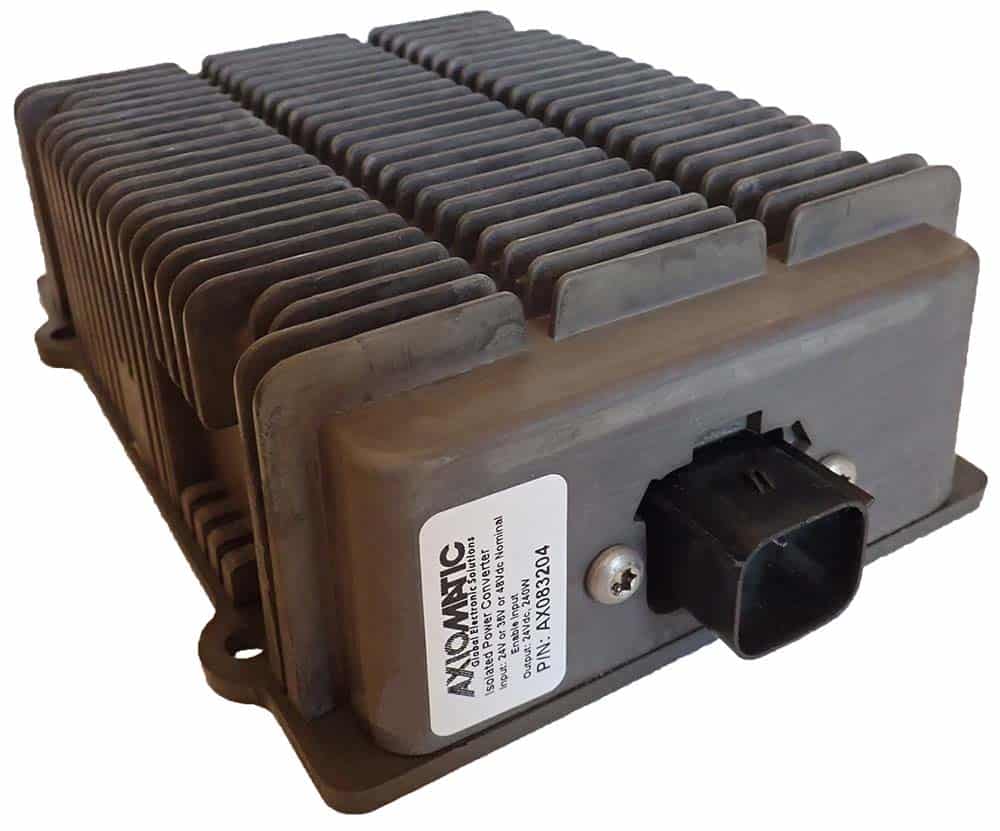
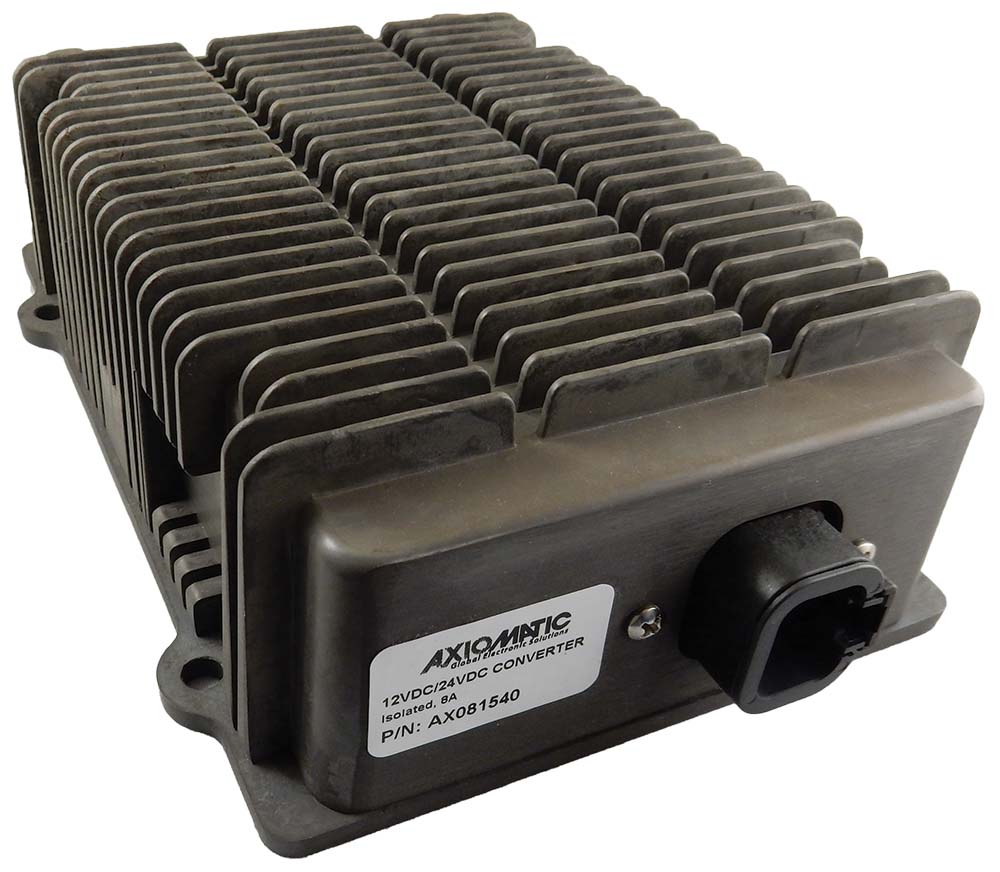
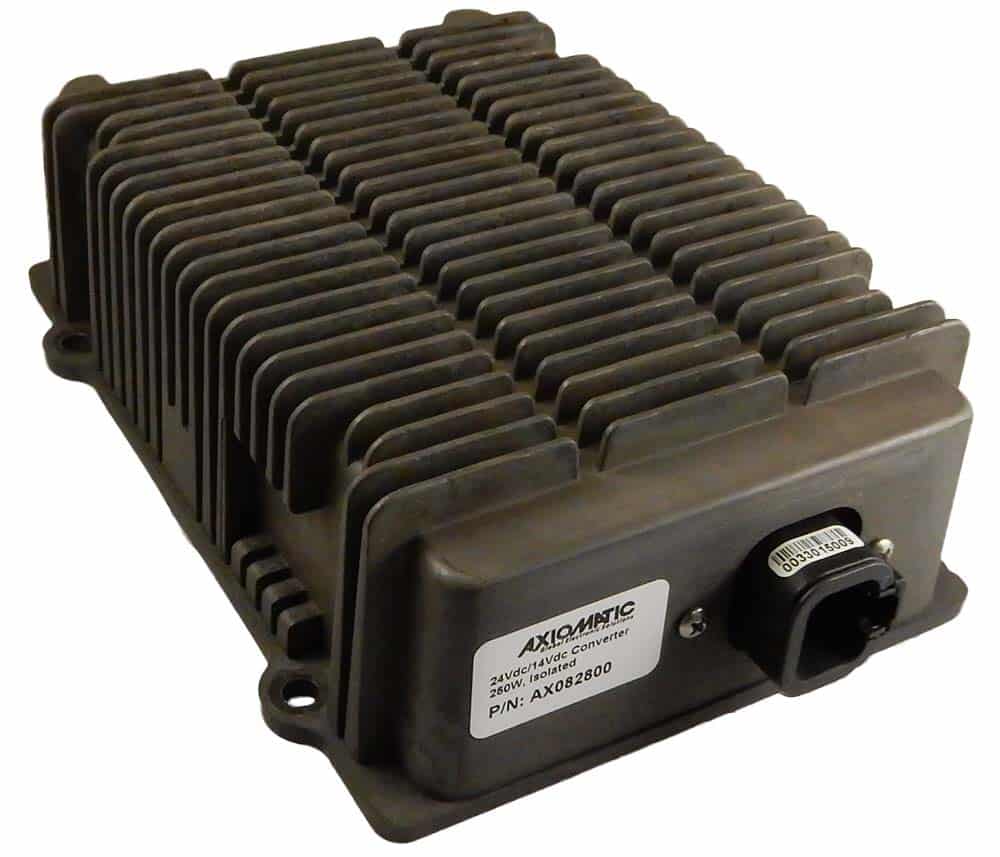
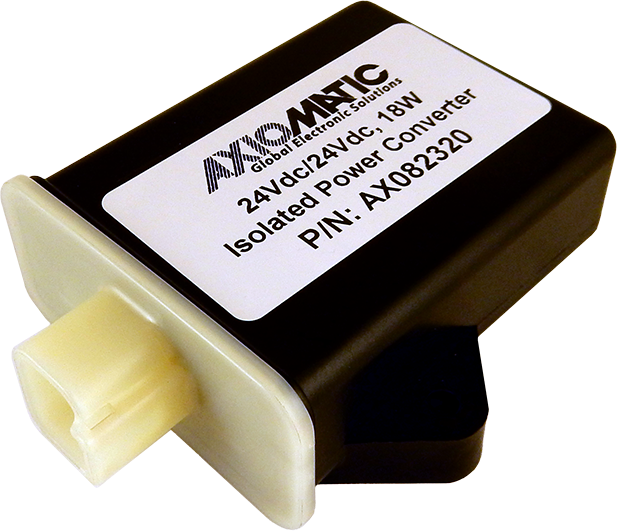
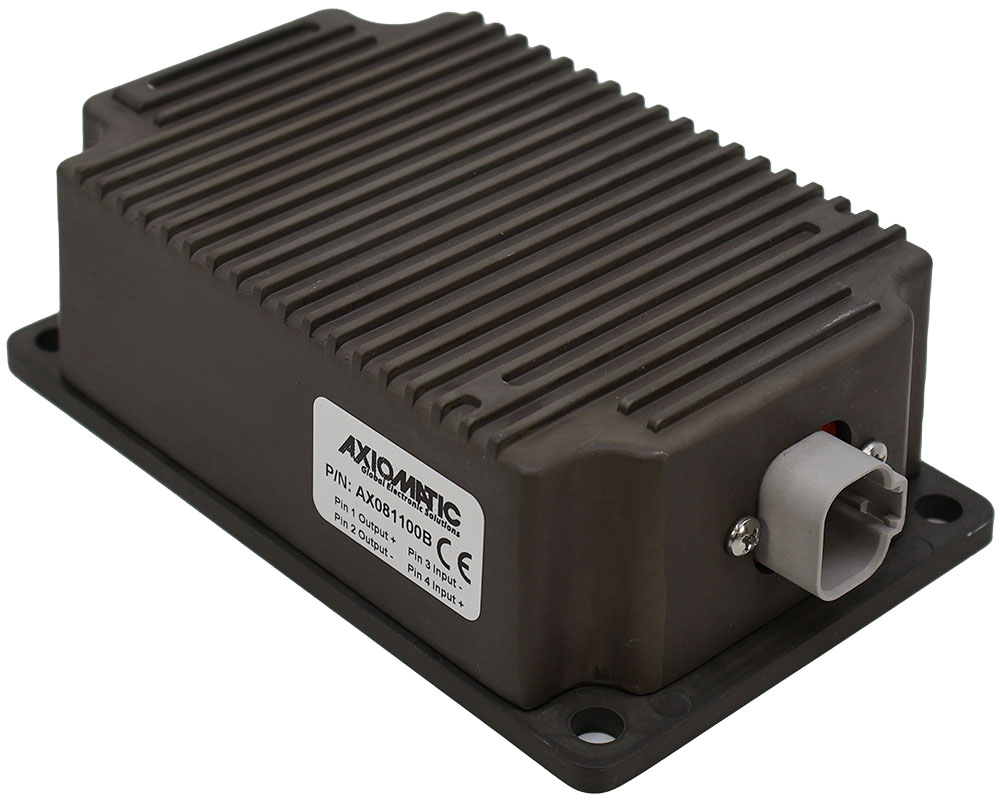
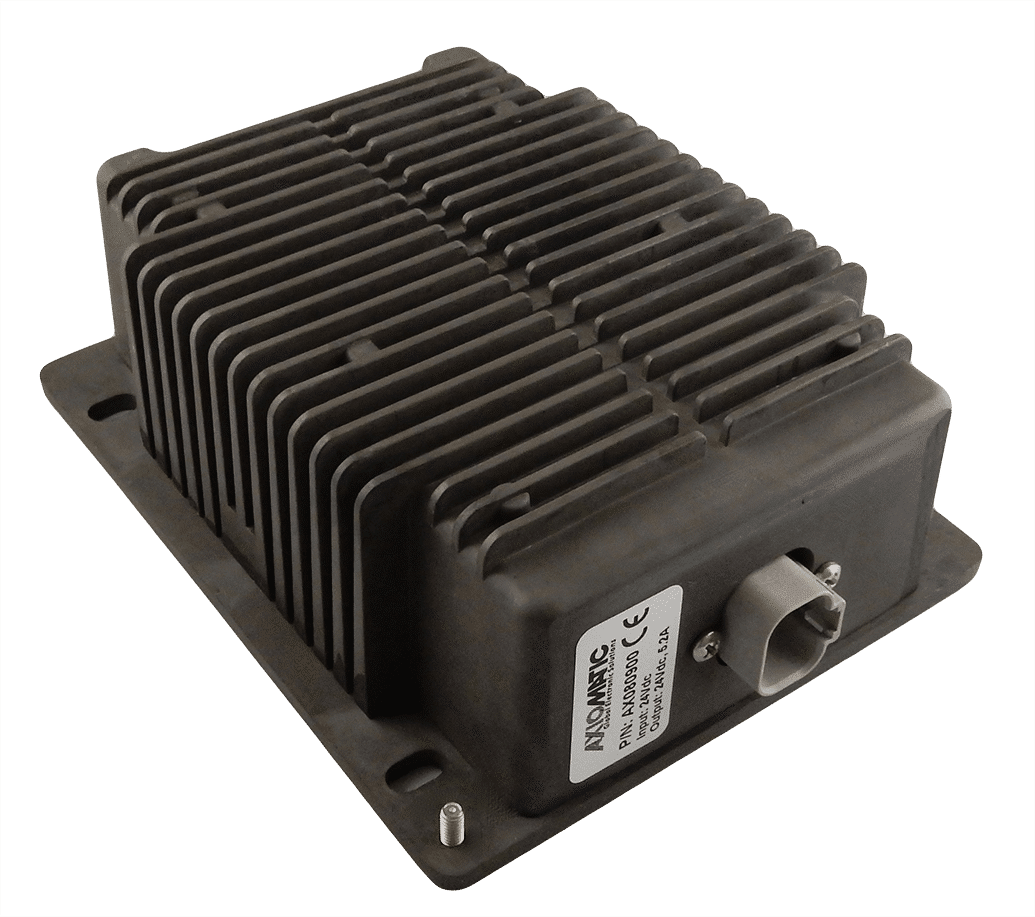
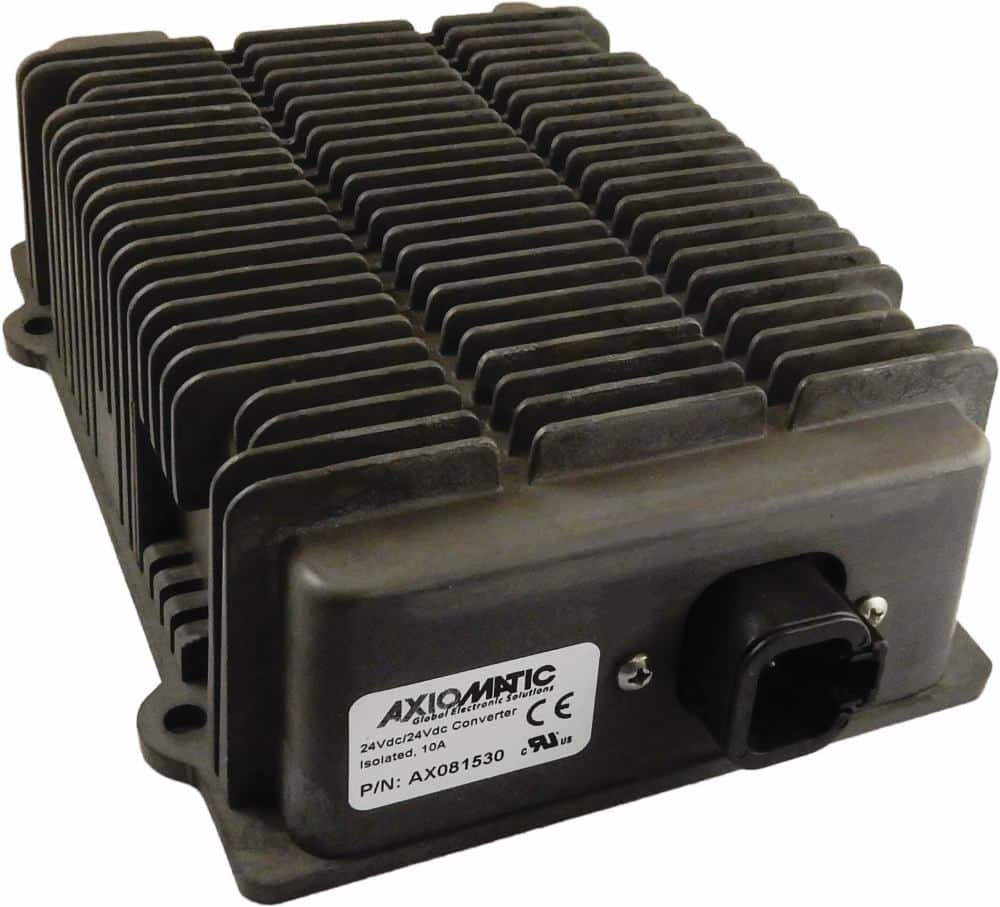
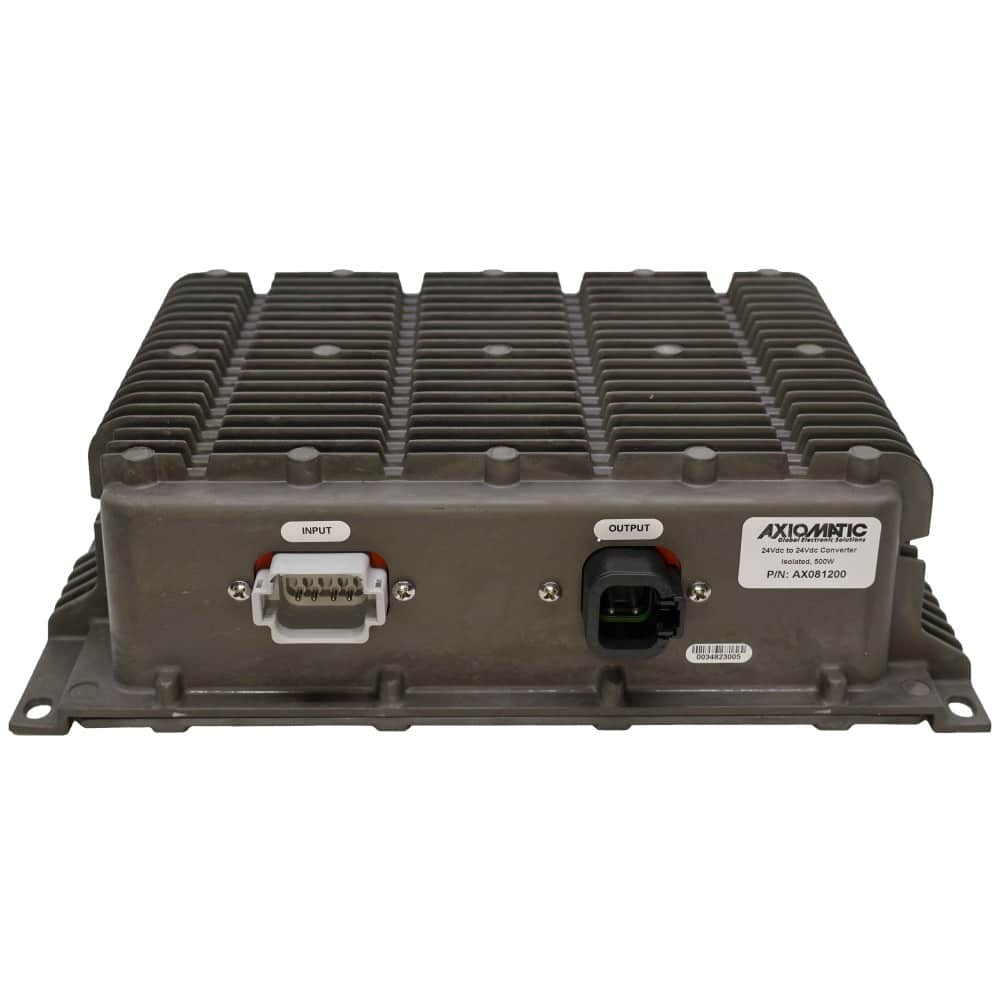
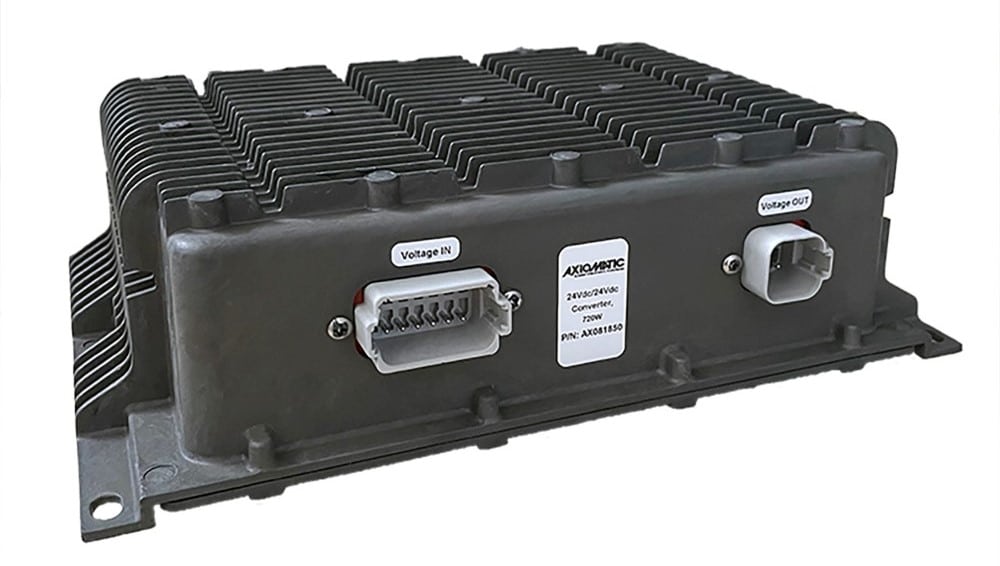
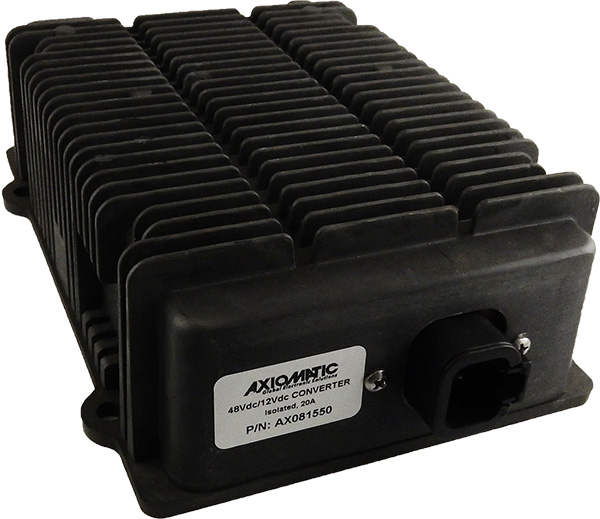
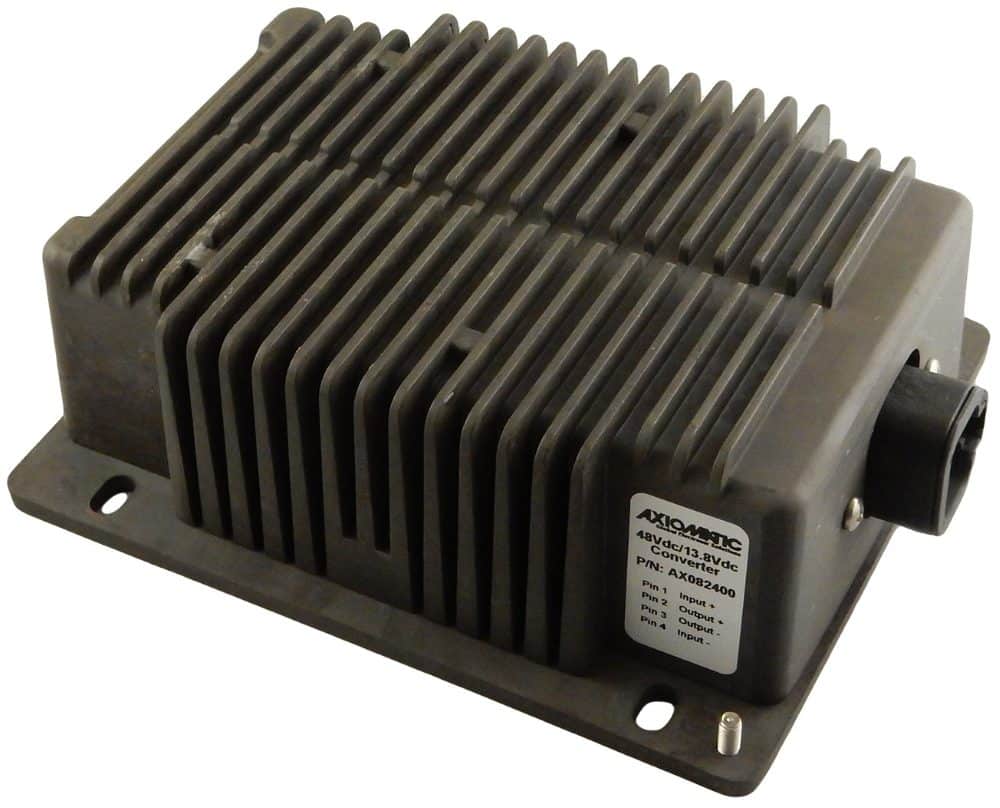
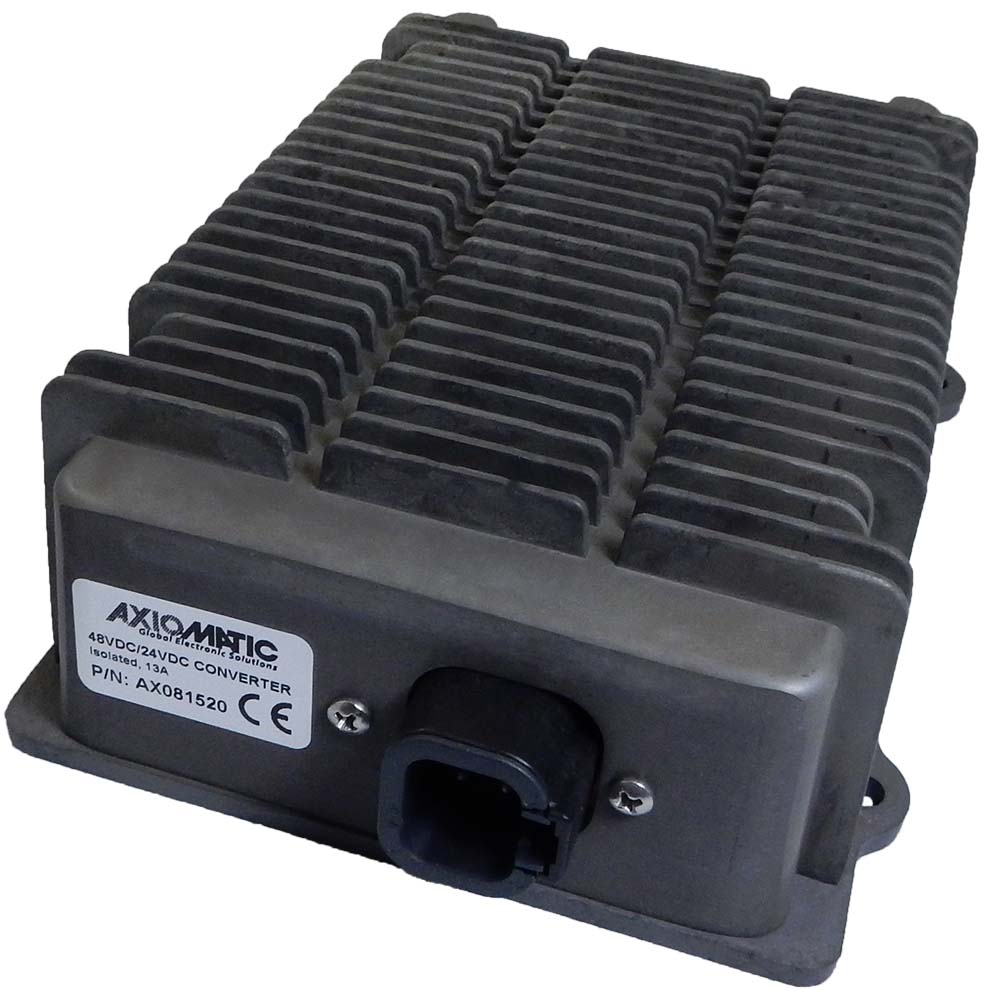
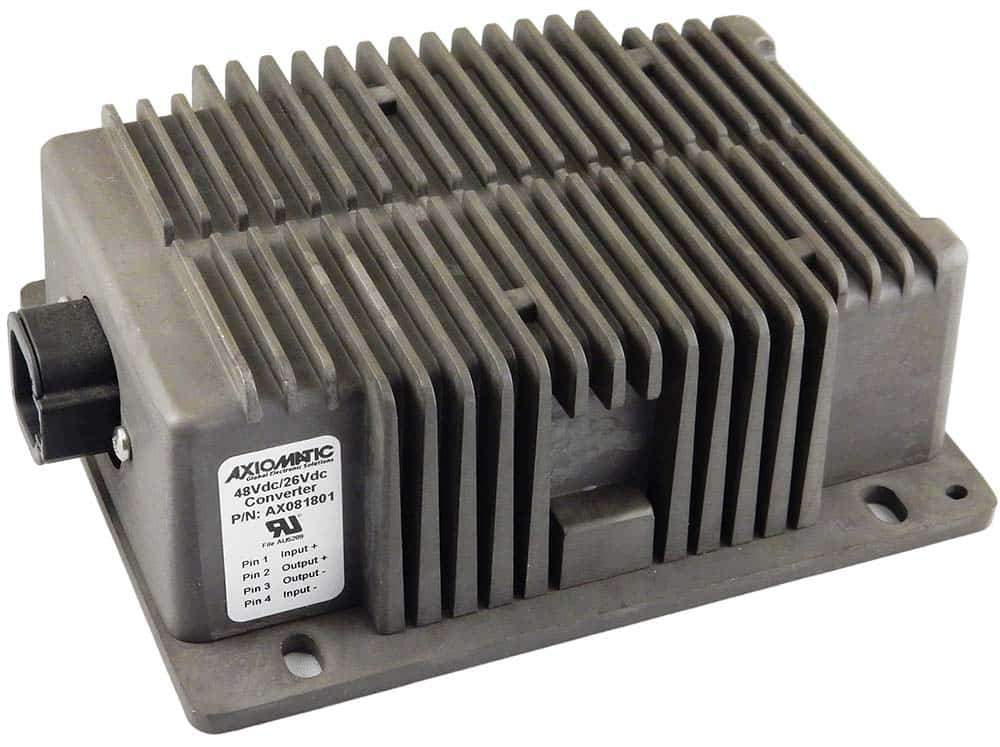
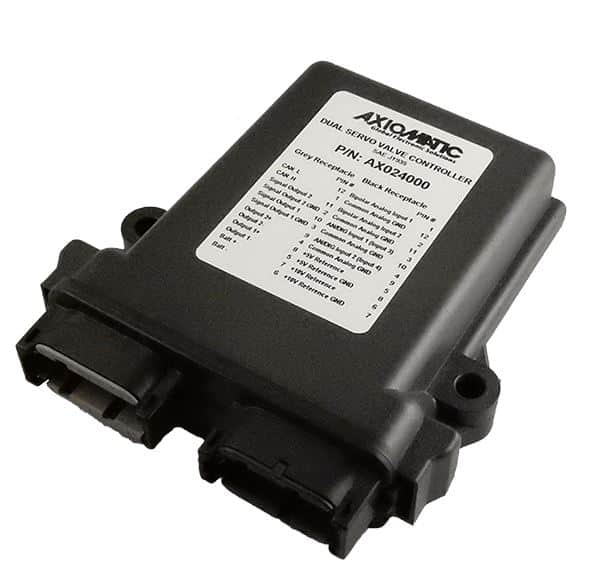
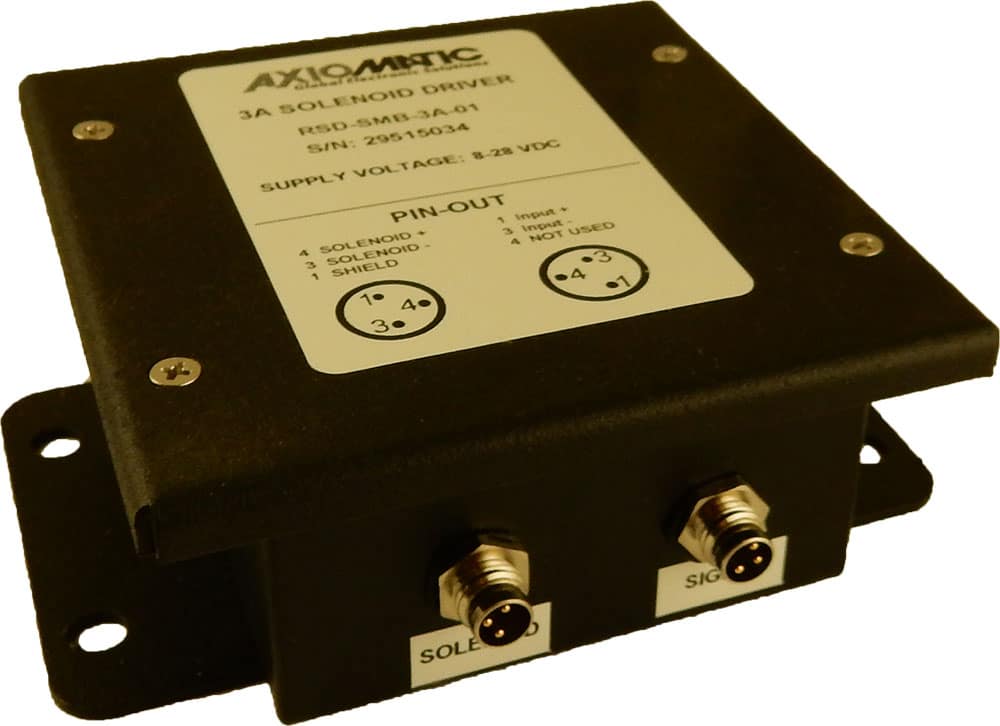
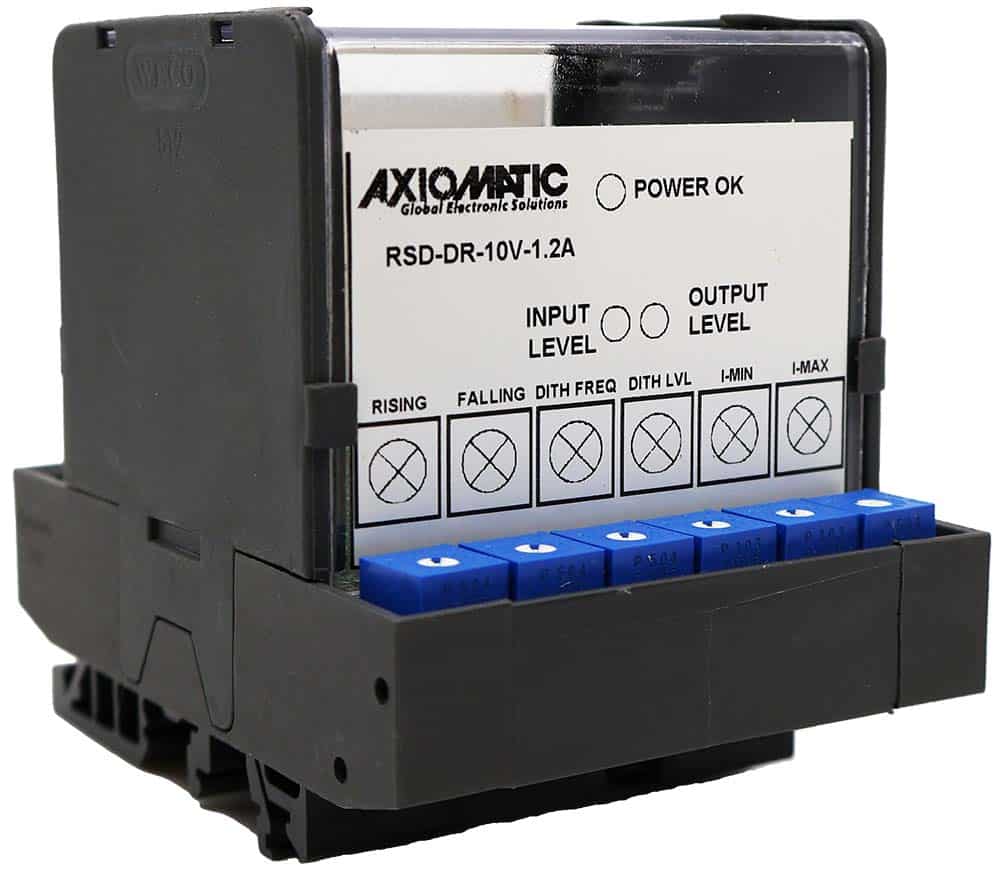
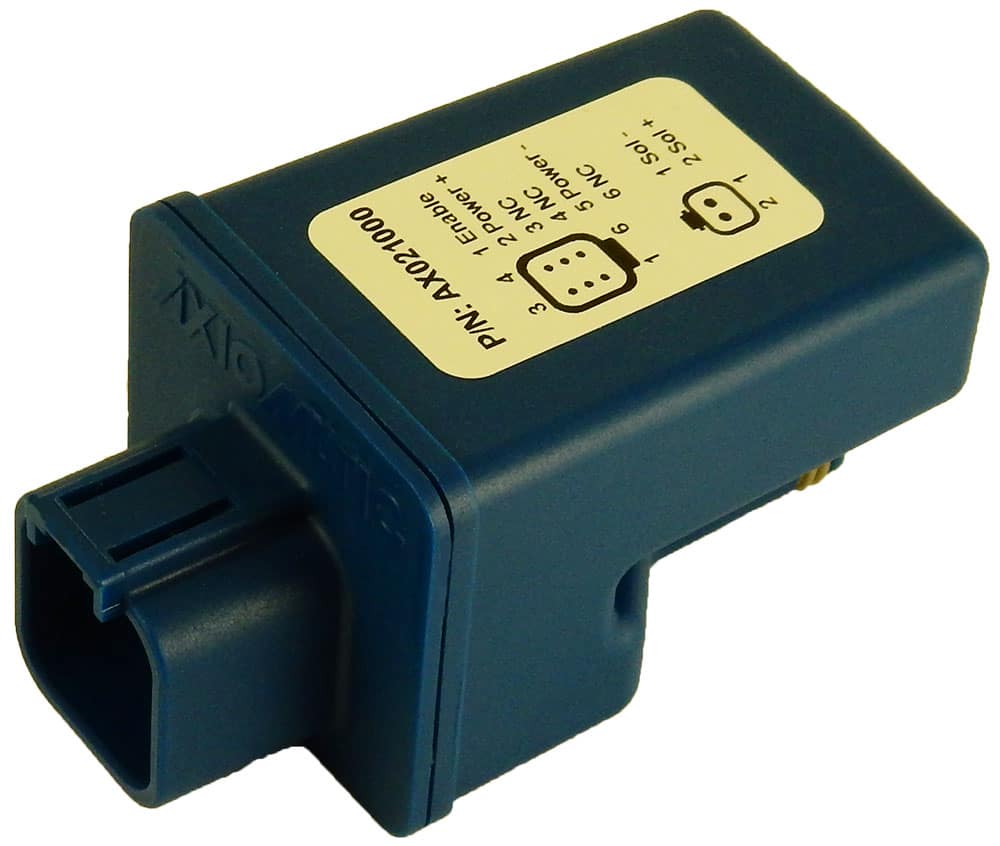
DC to DC Converters From Axiomatic
Axiomatic Technologies offers a comprehensive range of DC-to-DC converters designed to meet the power management needs of various industries, including mobile, industrial, and automation sectors. These converters are engineered to provide reliable and efficient voltage conversion, ensuring optimal performance of sensitive electronic systems. With a focus on ruggedness and adaptability, Axiomatic’s DC to DC converters are suitable for applications such as electric vehicles, construction machinery, and process control systems.
DC-DC Converters: Powering Precision in Demanding Applications
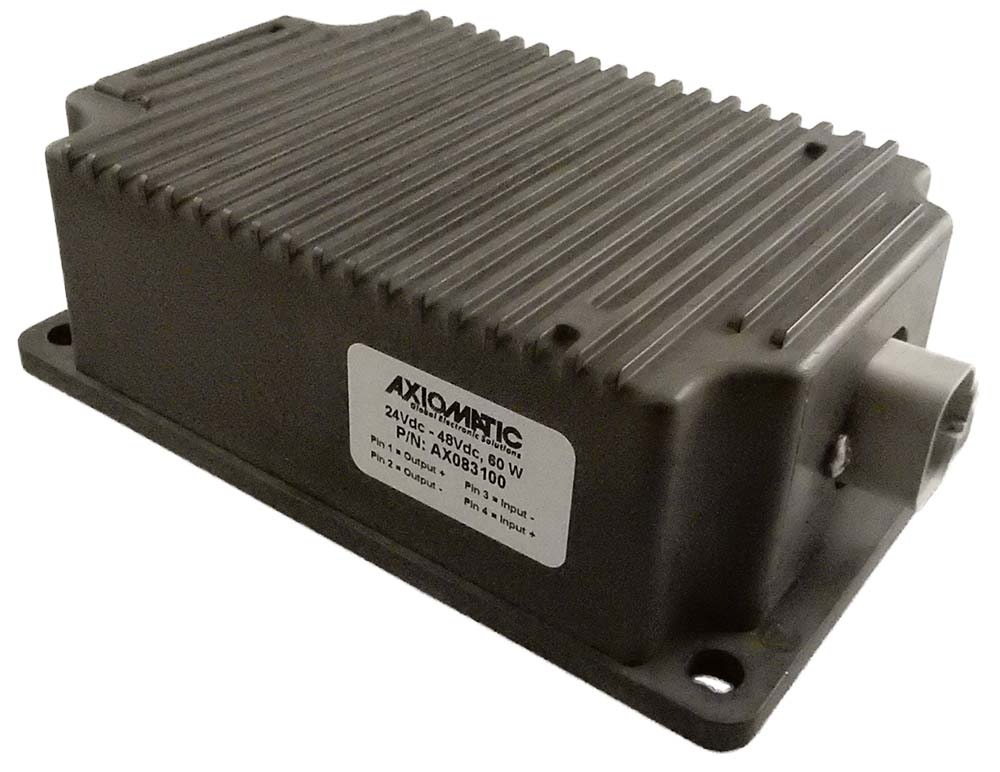
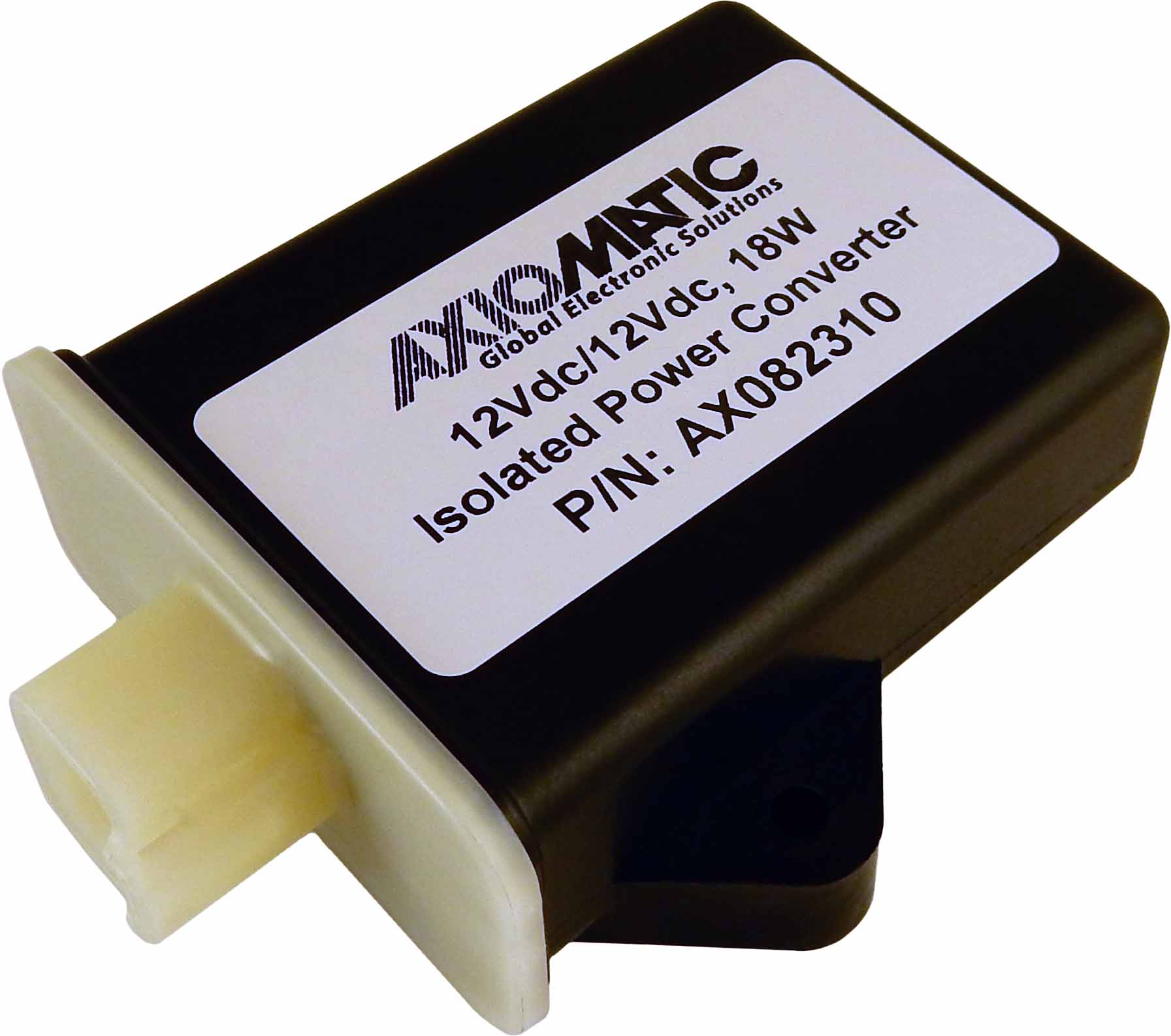
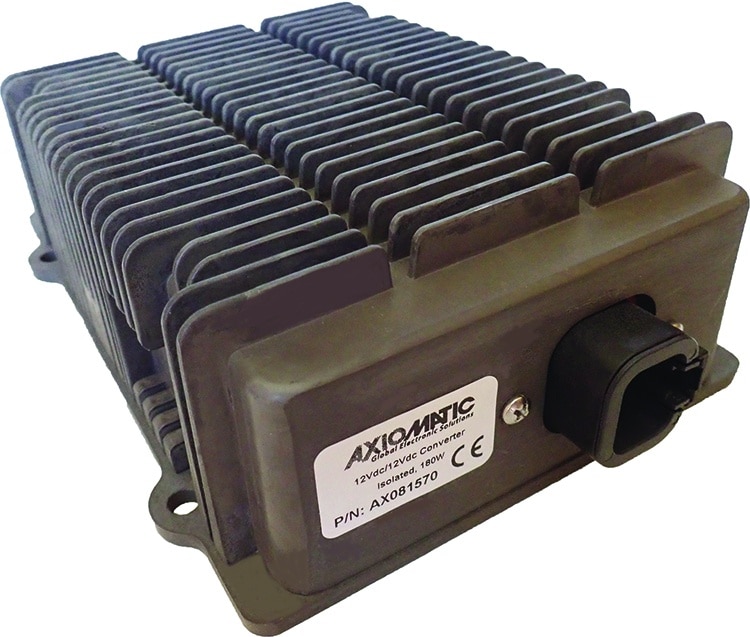
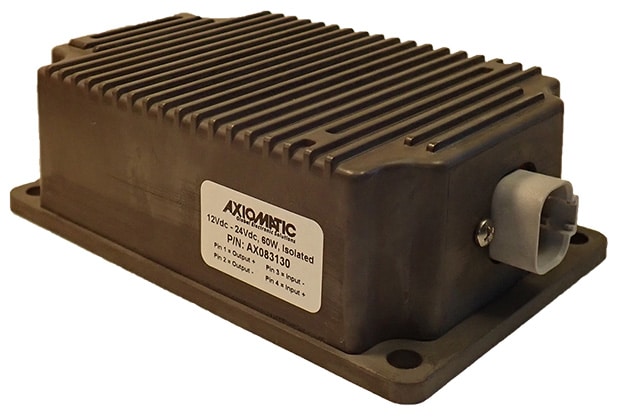
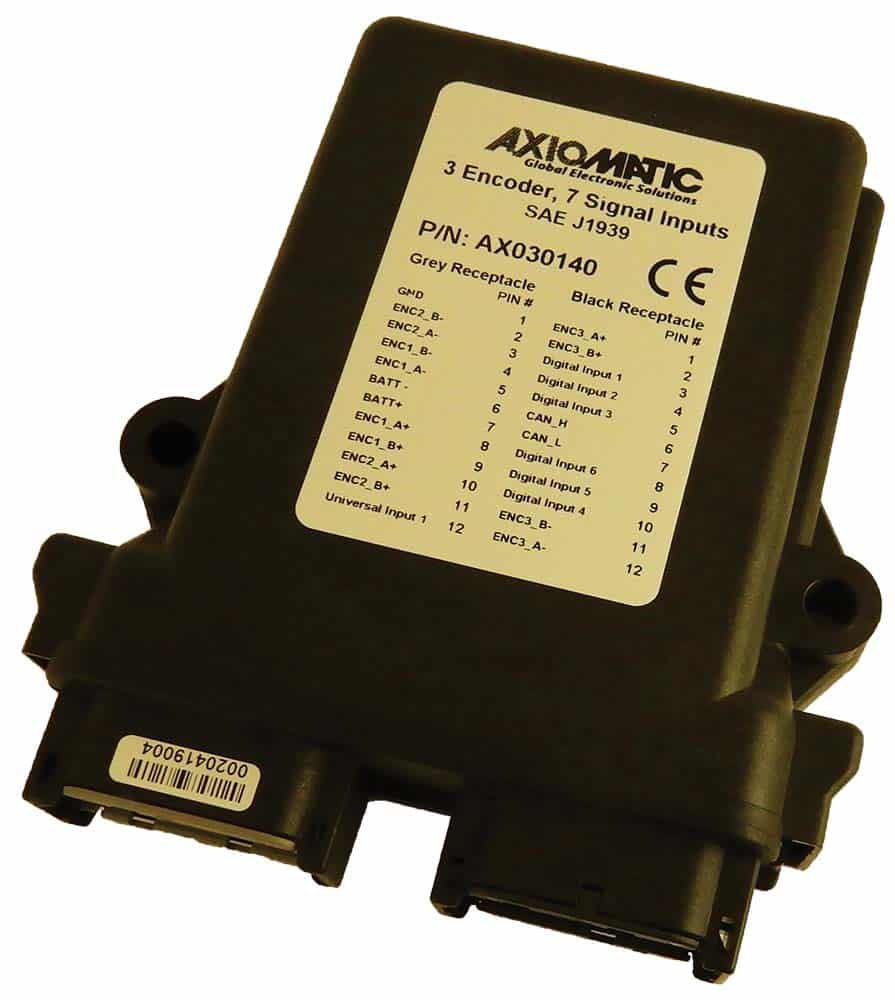
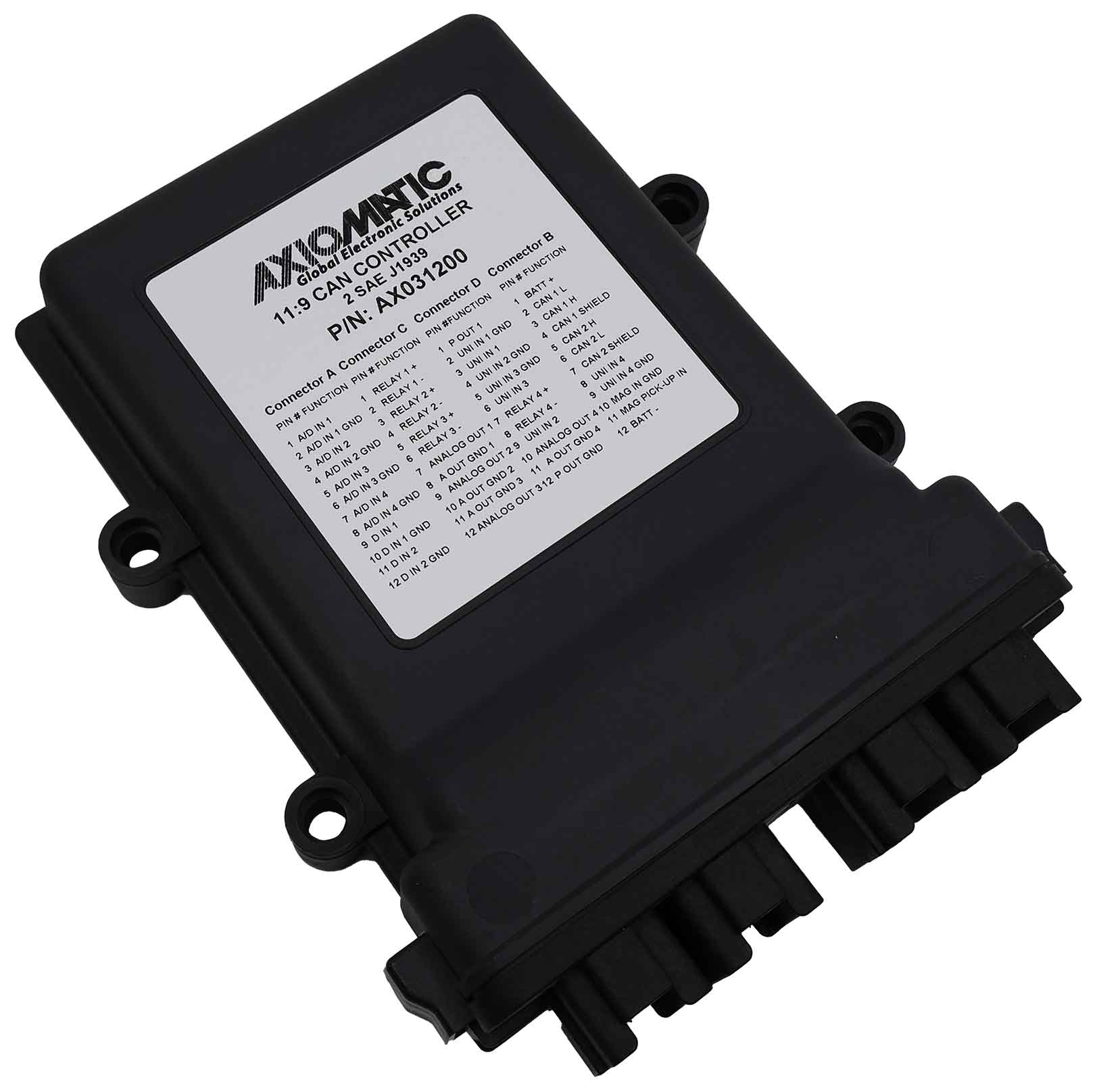
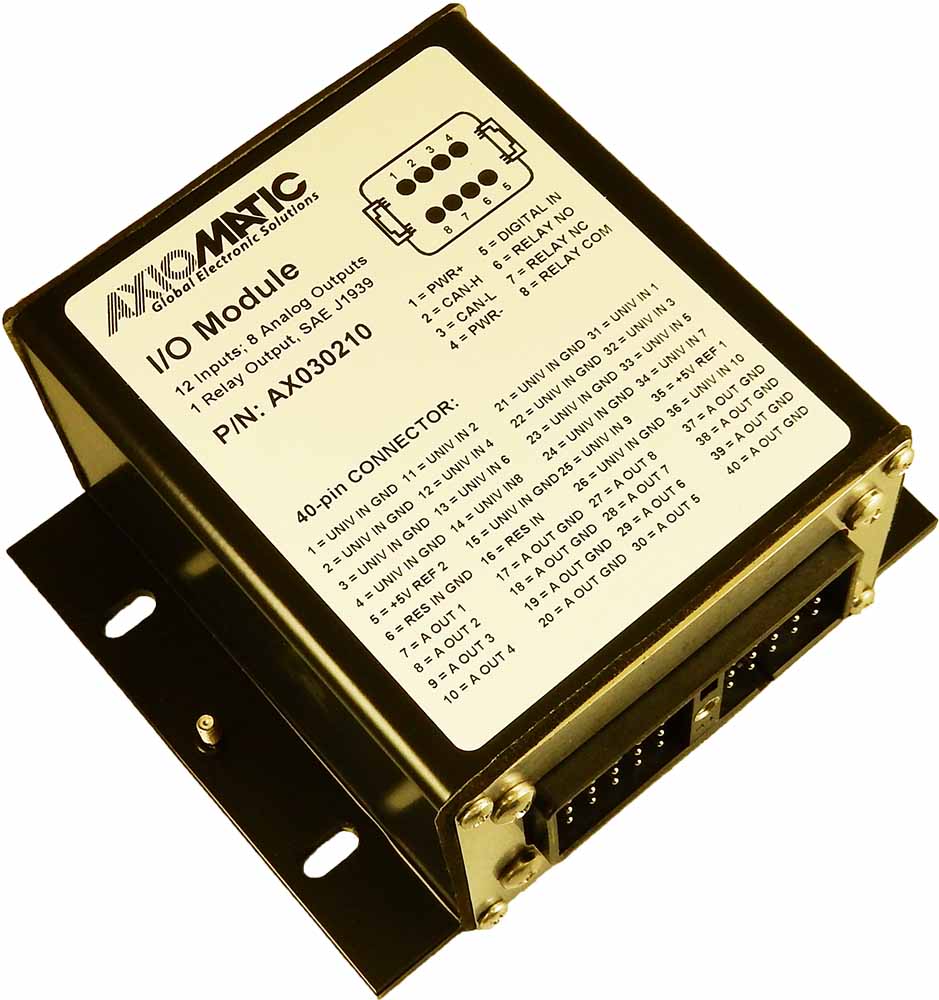
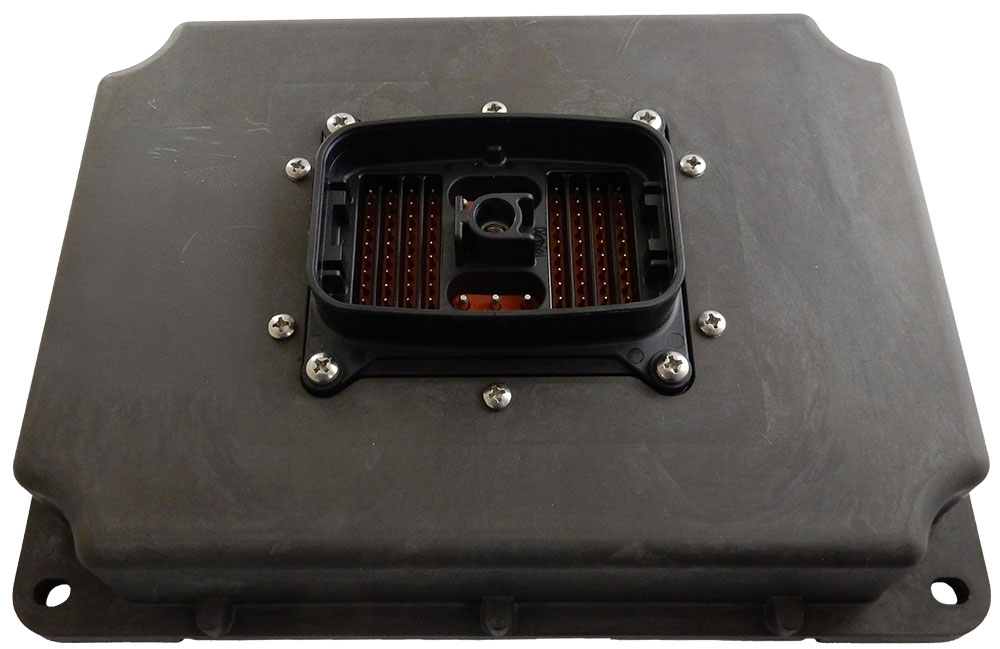
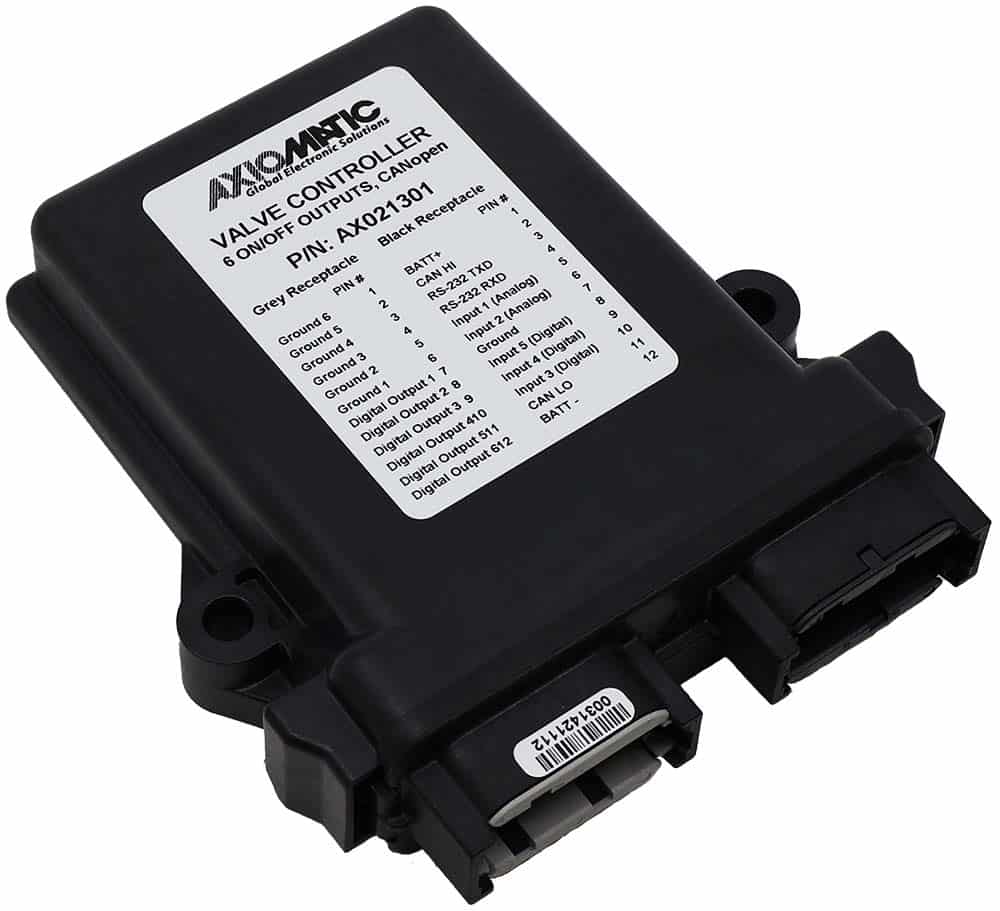
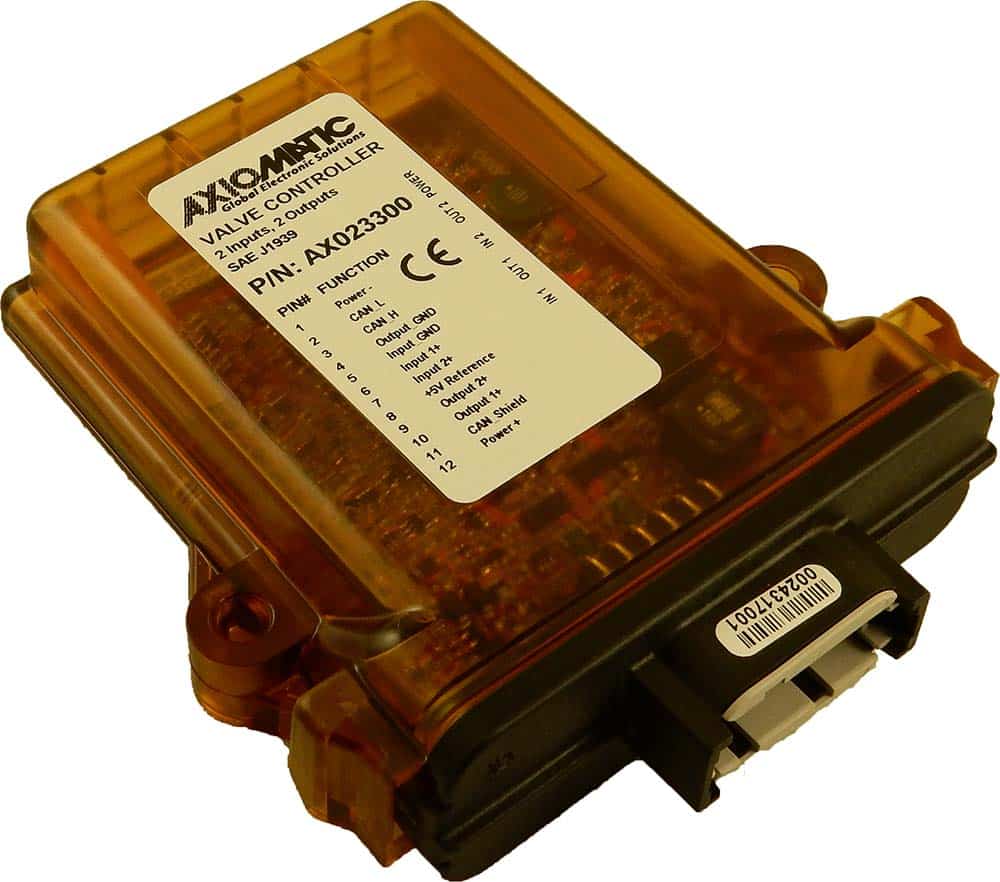
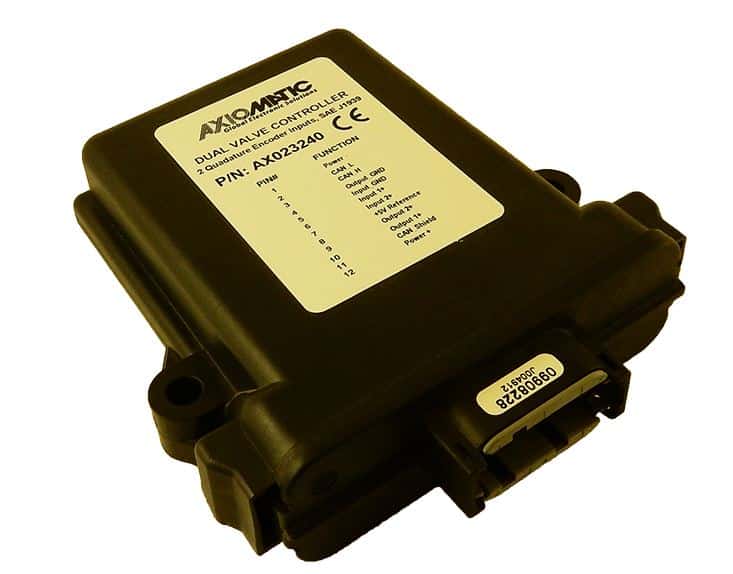
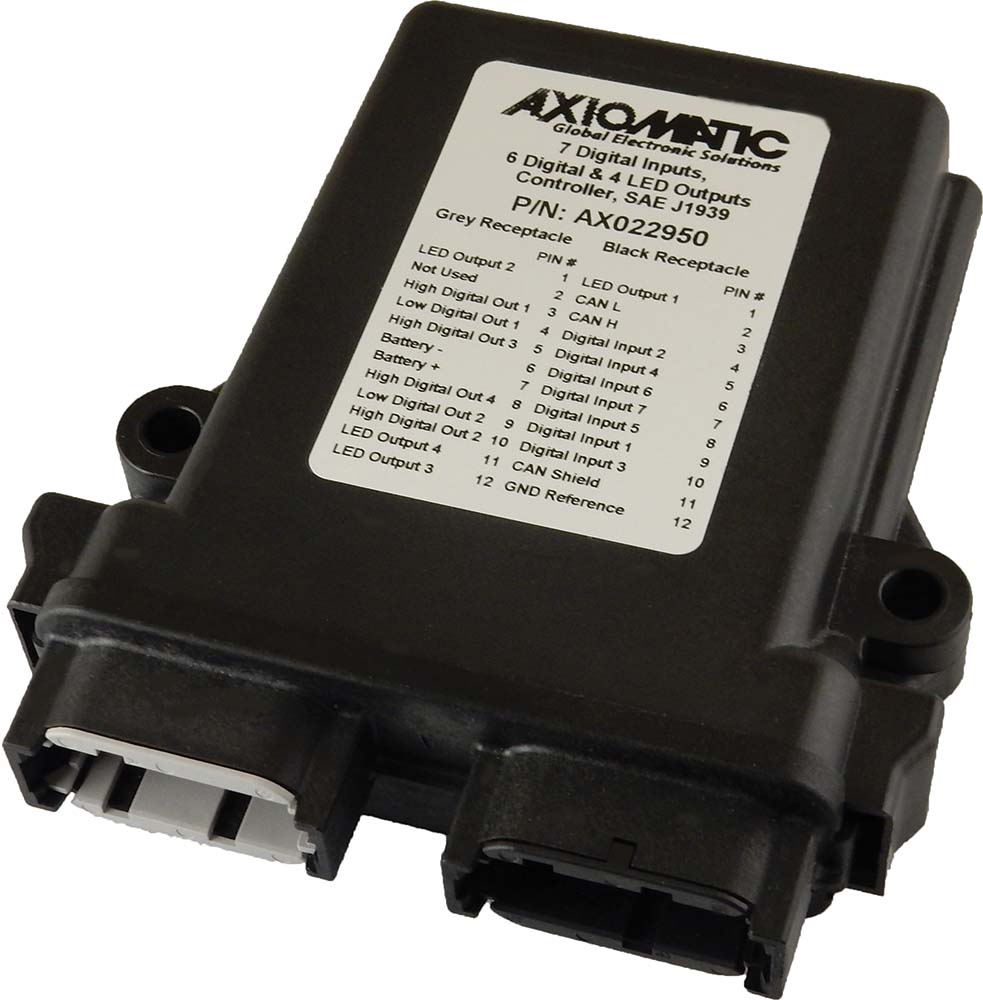
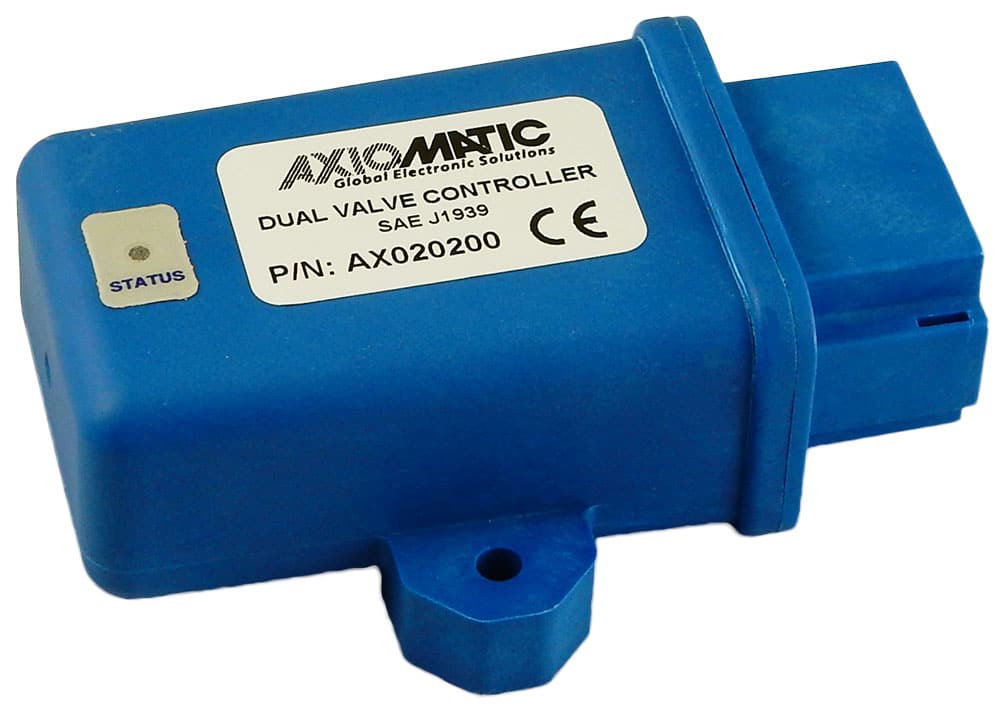
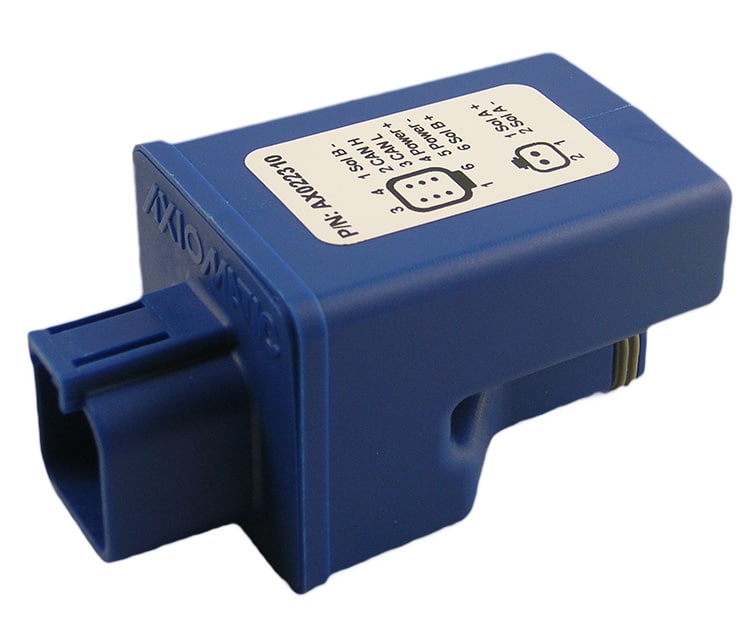
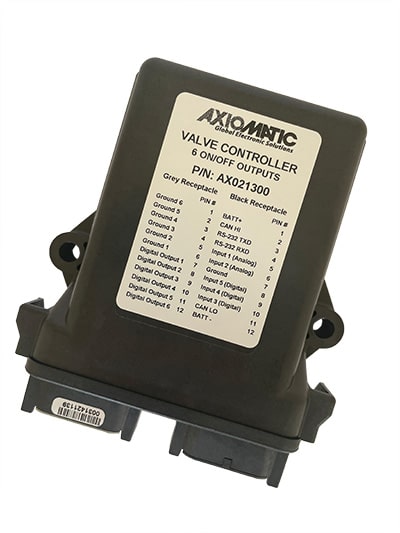
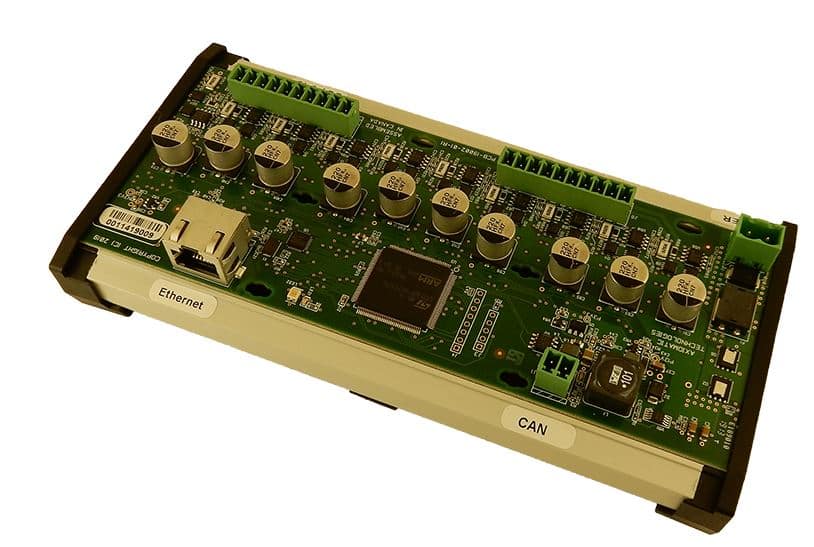
The product lineup includes isolated and non-isolated converters with varying input and output voltage configurations, such as 12V to 24V, 24V to 12V, and 48V to 24V. These DC to DC converters are designed to operate under harsh environmental conditions, featuring sealed enclosures that protect against moisture, shock, and vibration. Additionally, they incorporate advanced surge and transient suppression, over-voltage and under-voltage protection, and reverse polarity safeguards to ensure the longevity and reliability of connected equipment.
Axiomatic’s DC-DC converters also support communication protocols like CANopen® and SAE J1939, enabling seamless integration into complex control systems. For original equipment manufacturers (OEMs), Axiomatic provides customization options, including rapid prototyping and tailored solutions, to meet specific application requirements. This commitment to flexibility and innovation positions Axiomatic as a trusted partner for advanced power conversion solutions.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ) about DC-DC Converters
What is a DC-to-DC converter?
A DC-to-DC converter is an electronic device that converts a source of direct current (DC) from one voltage level to another, either stepping up (boost) or stepping down (buck) the voltage.
Why are isolated DC-DC converters important?
Isolated DC-DC converters provide electrical isolation between input and output, which protects sensitive equipment from voltage spikes and reduces the risk of ground loops in complex systems.
What are the typical applications of DC to DC converters?
DC to DC converters are used in various applications, including powering instrumentation and control networks, electric vehicles, robotics, and industrial automation systems, where stable and efficient voltage conversion is crucial.
How do Axiomatic’s DC-DC converters ensure reliability?
Axiomatic’s DC-DC converters are designed with rugged features such as sealed enclosures, surge and transient suppression, and protection against over-voltage, under-voltage, and reverse polarity, making them suitable for harsh operating environments.
Can Axiomatic’s DC-DC converters be customized for specific needs?
Yes, Axiomatic offers customization options for their DC-DC converters, including rapid prototyping and tailored solutions, to meet the unique requirements of OEMs and specific applications.
Are DC to DC Converters The Same As Buck Regulators or A Power Inverter?
A buck regulator is a converter that steps down the voltage. A power inverter and a DC-to-DC converter are related but fundamentally different devices in power electronics. A DC-DC converter changes one DC voltage level to another DC voltage level, either stepping it up or down while maintaining a DC output. In contrast, a power inverter converts DC power into AC power, producing an alternating current output typically used to run AC devices from a DC source such as a battery.
What is the difference between isolated and non-isolated DC-to-DC converters?
Isolated and non-isolated DC-to-DC converters differ primarily in their electrical separation between input and output circuits. An isolated power converter isolates the input from the output by electrically and physically separating the circuit into two sections preventing direct current flow between input and output, typically achieved by using a transformer. A non-isolated power converter has a single circuit in which current can flow between the input and output.
How do different DC converter topologies compare in terms of efficiency?
DC-to-DC Converter FAQ
What is the difference between isolated and non-isolated DC-to-DC converters?
Isolated and non-isolated DC-to-DC converters differ primarily in their electrical separation between input and output circuits. An isolated power converter isolates the input from the output by electrically and physically separating the circuit into two sections preventing direct current flow between input and output, typically achieved by using a transformer. A non-isolated power converter has a single circuit in which current can flow between the input and output.
Key Differences:
Safety & Protection:
For converters powered from high and potentially hazardous voltages (such as ac-dc converters powered from ac mains) isolation separates the output from dangerous voltages on the input.
In contrast, isolated converters alleviate safety concerns since the input and output sides are separated by a transformer, ensuring different grounds for the primary and secondary sides.
Performance & Efficiency:
The efficiency and regulation of non-isolated converters also tend to be better than that of an isolated converter.
A non-isolated power supply is usually >95 % efficient and more compact than an isolated one.
The disadvantage is low efficiency, and the package size is bigger than a non-isolated power supply due to the transformer needed for isolation.
Applications:
Isolated converters are essential for medical devices, heavy industrial applications, and systems requiring safety compliance
Non-isolated converters are commonly used in Point-of-Load (POL) applications and where isolation is already provided upstream
Design Complexity:
Non-isolated converters tend to be simpler and cheaper than isolated ones.
Isolated converters require transformers and additional components for feedback across the isolation barrier
How do different DC converter topologies compare in terms of efficiency?
DC converter efficiency varies significantly across different topologies, with switching converters generally outperforming linear regulators and some topologies excelling in specific applications.
Overall Efficiency Rankings:
Highest Efficiency (95-98%):
Of all these topologies, the synchronous buck SMPS is the most efficient.
Buck and boost converters use very few components, and this approach ensures they achieve high energy efficiency, typically up to 97 %.
High Efficiency (90-95%):
Non-isolated buck, boost, and buck-boost converters
A convenient method of replacing inefficient legacy linear regulters, the Traco TSR 1.5E series is a drop-in 1.5 A part that uses a buck step-down non-isolated topology to achieve efficiency up to 97 %.
Moderate Efficiency (75-90%):
A transformer introduces primary to secondary losses, so most flyback converters struggle to achieve better than 90 % energy efficiency.
Switching conversion is often more power-efficient (typical efficiency is 75% to 98%) than linear voltage regulation.
Topology-Specific Performance:
According to the evaluation results, the SI, SC and voltage-doubler topologies perform worse than the other options. Both solutions result in modified boost converters with limited gain and considerable voltage stress, which contributes to their poor efficiency.
According to the comparison findings, the modified boost converter that utilizes the VL technique can be deemed more appealing in terms of performance.
What are the requirements for automotive grade DC-to-DC converters?
Automotive grade DC-to-DC converters must meet stringent requirements to operate reliably in the harsh automotive environment, particularly with the rise of electric vehicles and advanced driver assistance systems (ADAS).
What does UL listed mean for industrial DC-to-DC converters?
UL listed industrial DC-to-DC converters have undergone rigorous testing and certification to meet safety standards for use in industrial applications, providing assurance of safe operation under specified conditions.
DC to DC Converters – Not Just for fuse protected battery chargers